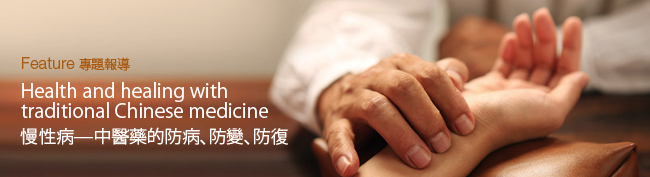
As defined by the World Health Organization, chronic diseases are diseases of long duration and generally slow progression. The four main types of chronic disease are cardiovascular diseases (e.g. heart attacks and strokes), cancers, chronic respiratory diseases (e.g. chronic obstructed pulmonary diseases and asthma) and diabetes. Chronic diseases are the leading cause of death worldwide, accounting for some 60% of all deaths.
Chinese medicine adopts a holistic approach to diagnosing and treating chronic diseases. It involves a systematic understanding of the human body and establishes personalised treatments based on specific dysfunctions of the body. Chinese medicine also stresses preventive measures, focusing on ways to prevent diseases, enhance each patient’s quality of life, and reduce fatality rates. |